Want to measure your company's carbon emissions? Here's what you need to know:
4 main ways to track carbon emissions:
| Method | Best For | Key Feature | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| GHG Protocol | Any size business | 3-scope framework | Free tools |
| ISO 14064 | Large companies | Step-by-step process | Higher costs |
| PAS 2050 | Product-focused | Tracks single items | Medium range |
| EcoHedge | Small-medium business | Automatic tracking | £999/year |
Quick comparison of tracking methods:
| Feature | GHG Protocol | ISO 14064 | PAS 2050 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | 3 scopes | 6 categories | Product lifecycle |
| Data Needed | Basic records | Detailed logs | Full product data |
| Verification | Optional | Required | Required |
| Complexity | Low | High | Medium |
Here's the thing: 75% of most companies' emissions come from their supply chain (Scope 3).
The numbers don't lie:
- 81% of S&P 500 companies report emissions
- 22,000+ companies worldwide track carbon
- Carbon tracking market growing 28.66% yearly
Bottom line: Pick GHG Protocol if you're starting out. Use ISO 14064 if you need detailed verification. Choose PAS 2050 for product-specific tracking. Go with EcoHedge if you want automation.
A YouTube Video Explaining the Concept of Scopes:
GHG Protocol: The Global Standard
The GHG Protocol splits emissions into three categories that every company needs to track:
| Scope | What It Measures | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Scope 1 | Direct emissions you control | Company vehicles, on-site fuel burning |
| Scope 2 | Indirect energy emissions | Purchased electricity, heating, cooling |
| Scope 3 | All other indirect emissions | Supply chain, business travel, waste |
Here's how companies use the Protocol to measure their carbon footprint:
1. Map Your Emissions
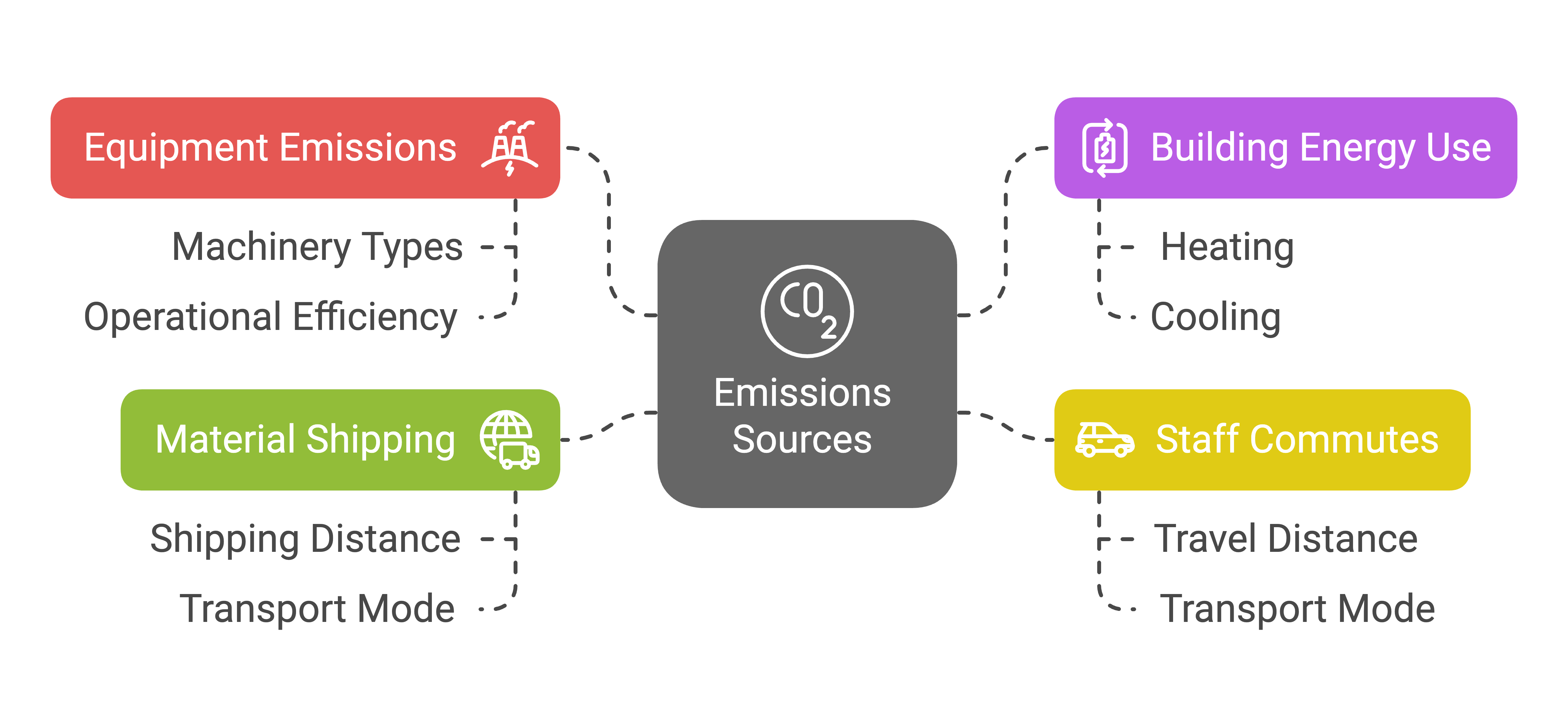
Key Steps to Mapping Emissions
Start by listing EVERY source of emissions across all scopes. For a factory, this means:
- Equipment emissions
- Building energy use
- Staff commutes
- Material shipping
2. Get Your Numbers
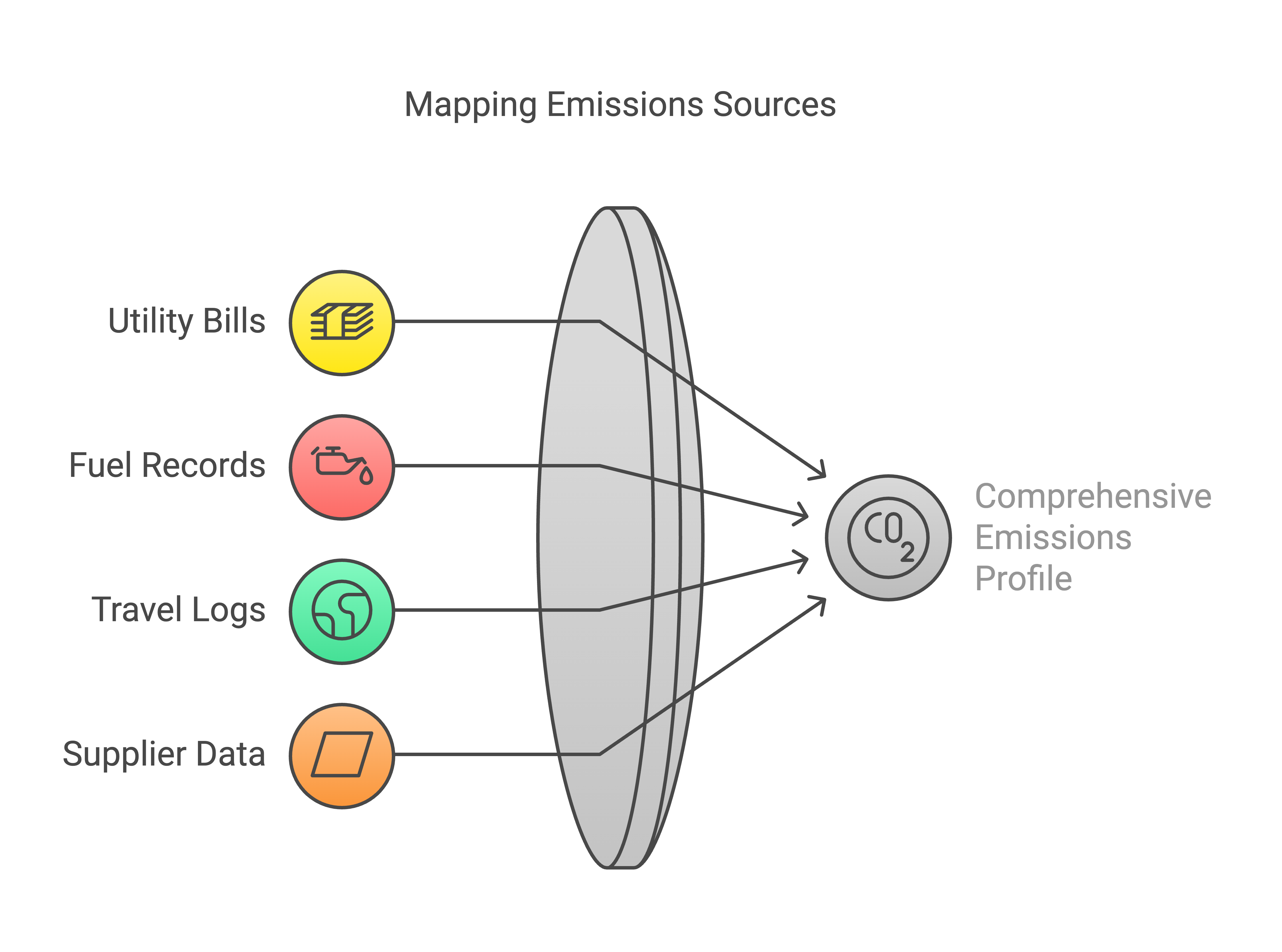
Pull data from:
- Utility bills
- Fuel records
- Travel logs
- Supplier data
3. Do The Math
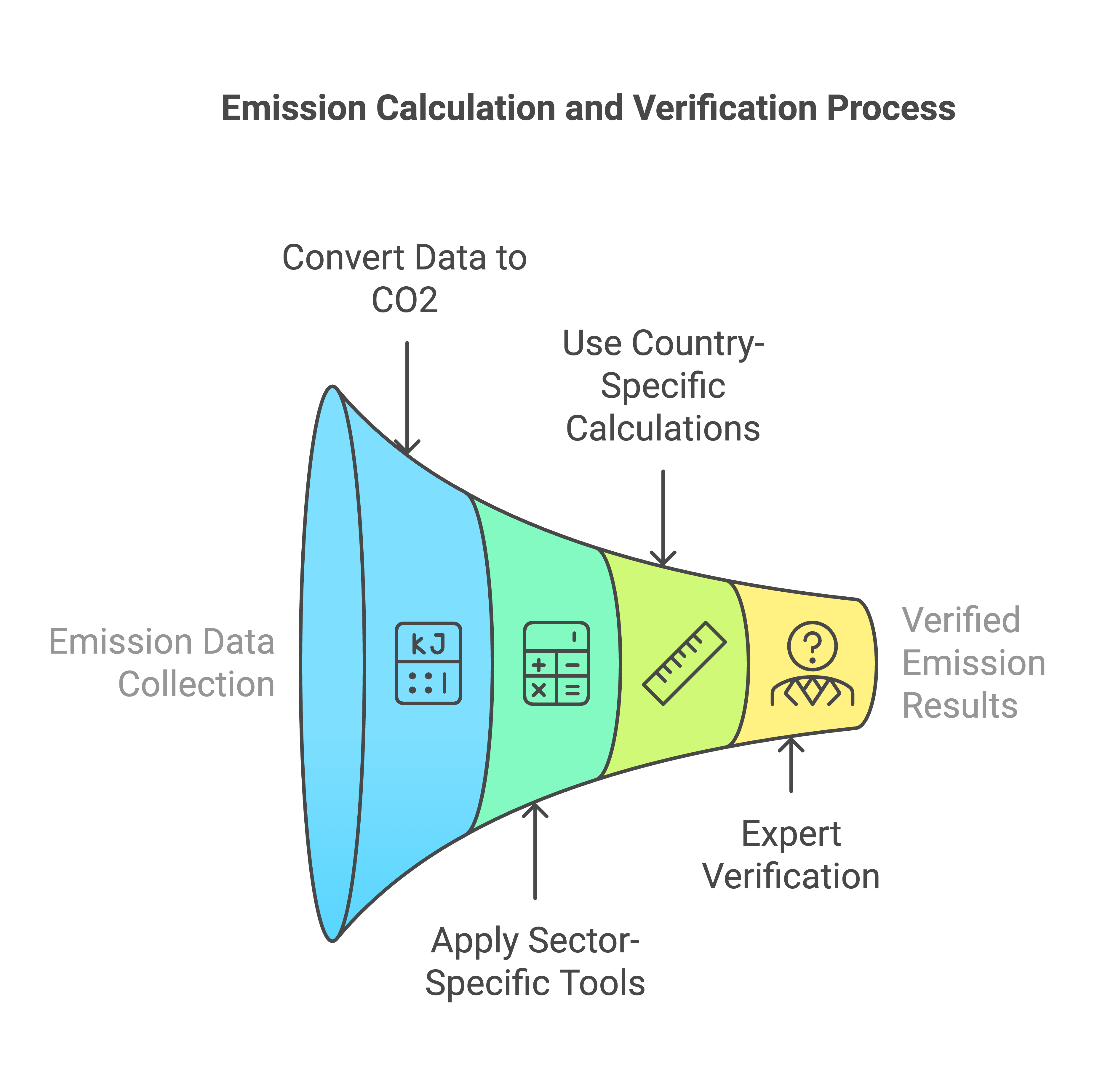
| Tool Type | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Cross-sector | Basic math for any business |
| Sector-specific | Special tools for industries like cement |
| Country-specific | Calculations based on local power grids |
The Protocol's impact? It's HUGE. 92% of Fortune 500 companies use it. And here's something that might surprise you: 75% of most companies' carbon footprint comes from Scope 3 emissions.
4. Get It Checked
You can't just calculate and call it done. The Protocol requires outside experts to:
- Look at your data
- Double-check calculations
- Sign off on results
These verified numbers let companies:
- Create carbon targets
- See if they're improving
- Show results to investors
- Meet government rules
Bottom line: The Protocol works because it's based on hard numbers and clear steps. It's carbon accounting made simple - no fluff, just facts.
2. ISO 14064: Step-by-Step Guidelines
ISO 14064 breaks down GHG emissions into six categories - it's simpler than the GHG Protocol's three scopes:
| Category | What It Measures | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Direct Emissions | Sources you control | Factory equipment, company cars |
| 2. Imported Energy | Energy you buy | Electricity, heating |
| 3. Transportation | Outside transport | Supplier deliveries, customer shipping |
| 4. Products Used | Making what you use | Raw materials production |
| 5. Product Usage | Customer emissions | When people use your products |
| 6. Other Sources | Everything else | Waste disposal, employee commuting |
Here's how to implement ISO 14064:
1. Pick Your Targets
Get your basics ready: utility bills, shipping logs, and supplier information. Know what you want to measure.
2. Set Your Limits
ISO 14064 gives you three options to define your measurement scope:
| Boundary Type | What's Included |
|---|---|
| Operational Control | Everything you run |
| Financial Control | Everything you own |
| Equity Share | Based on ownership % |
3. Get Your Numbers
Grab these for each category:
- Energy bills
- Fuel receipts
- Travel records
- Production data
4. Calculate Emissions
Turn your data into CO2 numbers. Here's how it works:
- 1 kWh electricity = X kg CO2
- 1 liter fuel = Y kg CO2
5. Verify Results
"Verification boosts GHG data accuracy and helps build better reduction plans", says Jun Ooi, ISO Lead Auditor with 11+ years of experience.
Verifiers check:
- Data quality
- Math accuracy
- Method correctness
ISO 14064 vs GHG Protocol - key differences:
| Feature | ISO 14064 | GHG Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | 6 categories | 3 scopes |
| Flexibility | Choose your methods | Set methods |
| Focus | Verification process | Calculation details |
| Requirements | Less strict | More detailed |
Your ISO 14064 results matter to:
- Investors
- Customers
- Regulators
- Carbon markets
3. PAS 2050: Product Carbon Measurement
PAS 2050 is the first standard for measuring a product's carbon footprint. Released by BSI in 2008, it tracks emissions throughout a product's life.
Here's what PAS 2050 measures at each stage:
| Life Cycle Stage | What to Measure | Data Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Extraction and processing | Supplier emissions data |
| Manufacturing | Production processes | Energy usage, waste data |
| Distribution | Transport and storage | Shipping records, fuel use |
| Usage | Customer product use | Product energy consumption |
| End-of-Life | Disposal or recycling | Waste management data |
The process works in 4 main steps:
1. Pick Your Scope
You'll need to decide what goes into your calculations:
- Manufacturing emissions
- What suppliers produce
- Moving products around
- How customers use products
2. Get Your Numbers
| Data Type | Sources |
|---|---|
| Primary Data | Energy bills, production logs |
| Secondary Data | Industry averages, emission factors |
| Supply Chain Data | Supplier reports, transport records |
3. Do The Math
PAS 2050 keeps it focused:
- Skips anything under 1% of total emissions
- Must cover 95% of the product's life
- Counts carbon storage up to 100 years
4. Check Your Work
You'll need outside experts to verify:
- Your numbers are right
- Your math adds up
- You kept good records
| Protocol Feature | PAS 2050 Requirement |
|---|---|
| Cut-off Level | <1% of emissions |
| Coverage | 95% minimum |
| Carbon Storage | Must be included |
| Verification | Third-party required |
The proof? An MDF study showed PAS 2050 measured -667.75 kg CO₂e, close to GHG Protocol's -658.42 kg CO₂e, while ISO 14067 showed 816.92 kg CO₂e.
Want to use PAS 2050? Here's what you need:
- EcoHedge software (£999/year)
- BSI verification
- Industry calculators
"The 2011 revision of PAS 2050 makes the methodology more relevant and accessible to a wider range of businesses", - Rob Smallcombe, EcoHedge founder
sbb-itb-919600f
4. EcoHedge: Automated Carbon Tracking
EcoHedge connects to your existing business tools to track carbon emissions automatically. It pulls data from 20+ accounting apps, so you don't have to do the work manually.
Here's what EcoHedge tracks:
| Category | What It Tracks | How It Works |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Emissions | Fuel use, company vehicles | Links to fuel cards, expense systems |
| Purchased Energy | Electricity, heating | Connects to utility accounts |
| Supply Chain | Supplier emissions | Pulls from accounting software |
| Business Travel | Flights, accommodation | Integrates with booking systems |
The software works in 3 steps:
1. Data Collection
EcoHedge automatically grabs data from your:
- Bank statements
- Utility bills
- Travel bookings
- Supplier invoices
2. Auto-Categorization
The system organizes your emissions like this:
| Emission Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Scope 1 | Gas, fleet fuel |
| Scope 2 | Bought electricity |
| Scope 3 | Business travel, purchases |
3. Report Generation
You'll get clear reports showing:
- Monthly emission totals
- Year-on-year changes
- Reduction targets
- GHG Protocol reports
Here's what you get:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Data Import | 20+ accounting app connections |
| Calculations | Built-in emission factors |
| Reporting | GHG Protocol aligned |
| Cost | £999/year |
"EcoHedge software makes carbon accounting as simple as financial accounting by automating data collection and calculations", - Rob Smallcombe, EcoHedge founder
The software supports major frameworks like GHG Protocol, ISO 14064, and PAS 2050 - perfect for businesses just starting with carbon tracking.
What Works and What Doesn't
Let's break down how different carbon tracking methods perform:
| Method | Works Well | Doesn't Work Well |
|---|---|---|
| GHG Protocol | • Clear scope definitions (1, 2, 3) • Flexible guidelines • Works for any company size |
• No formal certification • Less structured verification • Limited calculation guidance |
| ISO 14064 | • Third-party verification • Step-by-step framework • Strong data accuracy |
• Complex implementation • Higher costs • Time-intensive process |
| PAS 2050 | • Clear cut-off rules • Specific product focus • Carbon storage tracking |
• Limited to products only • Less suited for services • Requires 95% lifecycle data |
Here's what you need to know about data collection:
| Approach | Best For | Main Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Activity-Based | • Large companies • Detailed reporting needs • Regulatory compliance |
• High data requirements • More expensive • Takes longer |
| Spend-Based | • Small businesses • Quick assessments • Limited budgets |
• Less accurate • Based on averages • Missing specific details |
| Hybrid | • Mid-sized companies • Balanced approach • Getting started |
• More complex setup • Needs both data types • Higher initial effort |
Let's look at how different software options stack up:
| Software | Strong Points | Weak Points |
|---|---|---|
| Sweep | • L'Oreal and Burberry use it • Good for large companies • Strong supplier tracking |
• Limited reporting features • Higher price point • Complex setup |
| Watershed | • Used by FedEx and Walmart • Full sustainability tools • Good dashboards |
• Manual data entry needed • Service-dependent • Less automation |
| EcoHedge | • 20+ app connections • Quick setup • £999/year pricing |
• Newer platform • Limited features • UK-focused |
"The best carbon accounting software should match your company's size, budget, and data needs", says Rob Smallcombe, EcoHedge founder.
The numbers tell an interesting story. Take medium-density fiberboard production:
- PAS 2050: -667.75 kg CO2e
- GHG Protocol: -658.42 kg CO2e
- ISO 14067: 816.92 kg CO2e
Why such big differences? It comes down to three factors:
- Data inclusion rules
- Carbon storage calculations
- Process boundary definitions
Key Takeaways
Here's what different companies need for carbon tracking:
| Company Size | Best Method | Best Software | What You Get |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Business | GHG Protocol | EcoHedge | • Links to 20+ apps • Costs £999/year • Handles basic reports |
| Medium Business | Hybrid Approach | Watershed | • FedEx's top pick • Clear data views • Both auto and manual tracking |
| Large Enterprise | ISO 14064 | Persefoni | • Outside checks • Money-focused reports • Built for big companies |
Pick your tracking style based on what you need:
| What You Want | How to Do It | What to Expect |
|---|---|---|
| Fast Check | Spend-based | • 2-4 weeks to start • 70-80% right • Costs less |
| Deep Dive | Activity-based | • 8-12 weeks to start • 90%+ right • Costs more |
| Middle Ground | Hybrid | • 4-6 weeks to start • 80-85% right • Medium price |
The numbers show why this matters:
| What We See | The Facts |
|---|---|
| Market Growth | Up $9.61B by 2026 |
| How Fast | 28.66% yearly jump |
| Big Business | 92% of Fortune 500 use GHG Protocol |
| Who Reports | 8,400+ companies in 2019 |
"Pick carbon software that fits your size, money, and data needs", - Rob Smallcombe, who started EcoHedge.
What works:
- Use one tool for everything
- Start with Scope 1 and 2, add Scope 3 later
- Match your method to your data
- Get tools that work with what you have
- Think about outside checks
See how others did it:
| Who | What They Did | What Happened |
|---|---|---|
| IKEA | New bio glues | Cut climate impact 6% |
| L'Oreal | Uses Sweep | Better supplier data |
| Walmart | Picked Watershed | Full green tracking |
FAQs
What is the difference between PCF and LCA?
PCF focuses ONLY on carbon emissions, while LCA looks at ALL environmental impacts. Here's a breakdown:
| Aspect | Product Carbon Footprint (PCF) | Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Only GHG emissions | Multiple impacts (emissions, land use, ozone depletion) |
| Scope | Product-level carbon tracking | Full environmental analysis |
| Measurement | CO2 equivalents (CO2e) | Various environmental metrics |
| Analysis Type | Can be cradle-to-gate | Always cradle-to-grave |
| Time to Complete | Shorter | Longer |
Pick PCF when you need:
- Quick carbon numbers
- GHG Protocol reporting
- Product-specific emission data
Go with LCA if you want:
- A complete environmental picture
- Supply chain analysis
- ISO 14064 compliance
Bottom line: PCF gets you carbon data fast. LCA takes longer but shows every environmental impact.